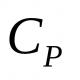Site sections
Editor's Choice:
- Sour cream and soy sauce sauce General principles for preparing batter for chops
- Cottage cheese casserole with apples
- Jellied pork ears recipe Why do you put pig ears in jellied meat?
- Canned saury: the benefits and harms of a famous seafood
- Gemini zodiac sign compatibility with other love signs
- Career Horoscope for April Aquarius
- Why see a snake on the road
- Successful combinations of numbers according to Feng Shui
- Who are godparents?
- Who has an advantage when downsizing?
Advertising
| Increased appetite and weight loss. Sudden weight loss: reasons for women. When weight loss should be a concern |
|
For breakfast, porridge with butter, for lunch, borscht with sour cream, schnitzel with potatoes, a piece of cake at night. With a minimum of physical activity, you lose weight. Weight fluctuations of one to three kilograms may not be noticed, but if you have quickly lost more than five percent of your body weight without dieting, it’s time to see a doctor. Rapid weight loss may be a sign of a serious illness. Losing weight: melting musclesOf course, weight fluctuations of 1-3 kg can be ignored; most often they are caused by changes in water-electrolyte balance, accumulation and loss of fluid. But if you quickly and without dieting have lost 5% of your body weight, you should consult a doctor and jointly analyze the reasons for the situation. Weight loss is the result of a lack of nutrients. A signal that the body begins to consume its own proteins, fats and carbohydrates to provide energy and maintain vital functions. . At the initial stage, weight loss is associated with the loss of fat mass, then the muscles begin to “melt” and other protein tissues, metabolism changes, functional and structural changes occur in organs, and diseases develop. Depression is the most common reason for weight lossDepression - mental disorder, manifested by a sharp and sustained decrease in mood, motor retardation, negative perception of reality and one’s own personality. One of the signs of depression is impaired taste perception, which results in decreased appetite and sudden weight loss. The situation is aggravated by the fact that the disease contributes to the development of gastritis and other diseases digestive system accompanied by abdominal discomfort. What to do if you notice signs of depression? Without delay, consult a doctor. Anyone. Start with a therapist. Depression is difficult to cope with on your own, and it cannot resist medication and psychotherapy. . In its advanced form, depression can lead to exhaustion and the emergence of suicidal thoughts. Hormonal disorders as a factor in weight lossSurely you have heard about the leading role of the hormonal system in the functioning of the human body, in particular in their influence on metabolic processes. Disorders of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid and pancreas can lead to increased metabolism and rapid weight loss. For example, patients with hyperthyroidism, along with anxiety, excitability, rapid heartbeat, dry skin, as a rule, have insufficient body weight with a sharply increased appetite. What to do? Run to an endocrinologist and take a biochemical blood test and a blood test for hormones of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract lead to weight lossThis list includes, first of all, celiac disease, enterocolitis, atrophic gastritis - that is, diseases accompanied by impaired absorption of nutrients. Inflammatory and atrophic processes occurring in the digestive tract lead to disruption of food digestion, and the accompanying abdominal pain, flatulence, constipation, and diarrhea discourage the desire to eat. An increasing deficiency of vitamins and microelements leads to dry skin, brittle and hair loss, thinning nails, and bleeding gums. What to do if weight loss is accompanied by abdominal discomfort and signs of hypovitaminosis? Contact and get examined. Only treatment of the underlying disease will allow you to return to normal weight. Diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas as a factor in weight lossChronic diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas go hand in hand. The reason for this is the proximity of the excretory ducts of these organs, causing a disruption in the flow of their enzymes into the intestines. Lack of digestive juices leads to insufficient breakdown of food and the occurrence of nutritional deficiencies in the body, despite adequate nutrition. Diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas are often accompanied by pain in the upper abdomen, changes in stool, and the appearance of a fatty film on the surface of stool. What to do if you suspect the cause of weight loss is a disease of the biliary system and pancreas? Contact a gastroenterologist for a full examination and treatment. Enzyme preparations will help normalize digestion. Causes of weight loss such as viral hepatitis or HIV cannot be ruled out; moreover, weight loss sometimes becomes the first symptom of the disease. Another infectious cause of weight loss is tuberculosis. In addition to the fact that due to intoxication, patients lose their appetite, fighting infection requires enormous energy expenditure, and the body takes it from its own reserves. Frequent coughing, constant low-grade body temperature, sweating, and weakness should suggest tuberculosis and become a reason for an emergency examination. Helminth infections, despite popular belief, rarely lead to significant weight loss. Exceptions are cases when the number of helminths “goes off scale”, and their presence causes intoxication and digestive disorders. There is such a thing as cancer cachexia - a condition of sudden weight loss caused by a malignant tumor. In most cases, doctors encounter it in the later stages of cancer development; with tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, this condition develops earlier. Patients suffer from intoxication, their appetite is disrupted, and taste sensations change. A rapidly growing tumor requires a huge amount of nutrients, as a result of which healthy tissues of the body begin to lack them. In addition, the substances secreted by the tumor have a toxic effect on the body’s tissues, slowing down metabolic processes in them and leading them to atrophy. As a result, with normal nutrition, a cancer patient begins to lose weight, and loses not only fat, but also muscle mass. The presence of constant weakness and low-grade fever, combined with unmotivated weight loss, should be a reason to consult a doctor. Start with , if necessary, he will refer you to an oncologist. In this situation, only comprehensive treatment will help. " />Weight loss is not always desirable or beneficial. Excessive weight loss for no apparent reason may be dangerous sign requiring consultation with a doctor. The main mechanisms for weight loss can be:1. Fasting or malnutrition.2. Reduced absorption of nutrients. 3. Increased needs of the body (stress, illness). Weight loss can be caused by a variety of infectious, oncological, gastrointestinal, metabolic, neurological diseases and various nutritional and vitamin deficiencies. Medical reasons for weight loss include:1. Anorexia nervosa, or anorexia nervosa. This is a psychogenic disease characteristic of young women, which is manifested by severe weight loss (from 10 to 50% of weight loss). initial weight). Patients experience hypotension, weakness, muscle atrophy, loss of adipose tissue, constipation, dental caries, susceptibility to infections, cold intolerance, hair loss, and amenorrhea.Patients usually express concern about possible weight gain. They can exhaust themselves with exercise, induce vomiting after eating, and use laxatives and diuretics. 2. Adrenal insufficiency. In this case, weight loss is accompanied by weakness, anorexia, irritability, nausea, abdominal pain, and bowel dysfunction. Skin hyperpigmentation may occur. 3. Cryptosporidiosis. This opportunistic protozoal infection can cause weight loss, watery diarrhea, abdominal cramps, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, fever and muscle pain. 4. Depression. Severe depression leads to loss of appetite and weight loss. Depression usually manifests itself as drowsiness, apathy, fatigue, pessimistic thinking, a feeling of hopelessness, lack of desire for any achievements, and sometimes suicidal thoughts. 5. Diabetes mellitus. With this disease, both weight gain and weight loss can be observed. Weight loss can occur even with increased appetite. The disease is accompanied by symptoms such as severe thirst, increased urine output, fatigue, weakness, etc. 6. Esophagitis. Painful inflammation of the esophagus causes the patient to avoid eating, which leads to weight loss. Intense pain in the front chest and in the mouth is accompanied by hypersalivation, difficulty swallowing, and rapid breathing. Sometimes vomiting with blood is observed. If a stricture (narrowing) develops, then swallowing problems and weight loss can be a constant concern. 8. Herpes (Herpes simplex virus type 1). With a herpes infection, painful, fluid-filled blisters around the mouth make eating unpleasant. This sometimes leads to malnutrition and weight loss. 9. Oncological diseases. Weight loss can be a sign of many types of cancer. Other symptoms may include the following: fatigue, nausea, fever, anorexia, bleeding. Cancer symptoms vary greatly depending on the type of cancer and its location. 10. Leukemia (blood cancer). Acute leukemia causes progressive weight loss, which is accompanied by weakness, fever, bleeding gums and other signs of bleeding disorders. Shortness of breath, tachycardia, abdominal and bone pain may also occur. As acute leukemia progresses, neurological symptoms may develop. Chronic leukemia also causes weight loss, fatigue, enlarged spleen, bleeding, anemia, skin lesions, and fever. 11. Lymphoma. Hodgkin's disease (Hodgkin's lymphoma) can cause gradual weight loss. Associated symptoms include fever, fatigue, enlarged spleen and liver (hepatosplenomegaly), and swollen and tender lymph nodes. Itchy skin may also develop. 12. Pulmonary tuberculosis. This infectious disease causes anorexia, gradual weight loss, weakness, fatigue, night sweats, and low-grade fever. Other manifestations of tuberculosis include: cough, mucopurulent sputum, hemoptysis, shortness of breath, chest pain. 13. Stomatitis. Inflammation of the oral mucosa during stomatitis prevents patients from eating normally, which leads to weight loss. The mucous membrane is usually red, swollen, and ulcerated. The disease is accompanied by fever (not always), hypersalivation, pain in the mouth, bleeding gums, etc. 14. Thyrotoxicosis. With thyrotoxicosis, the level of thyroid hormones increases. This causes increased metabolism and weight loss. Other characteristic symptoms include: nervousness, heat intolerance, diarrhea, increased appetite, palpitations, sweating, trembling limbs. It is also possible to have an enlarged thyroid gland and exophthalmos (protrusion of the eyeballs). 15. Crohn's disease. With Crohn's disease, weight loss can be combined with pain and cramps in the abdomen, and lack of appetite. Patients may complain of diarrhea, nausea, fever, tachycardia, rumbling in the stomach, weakness and fatigue. 16. Ulcerative colitis. With this disease, weight loss is accompanied by abdominal pain, diarrhea mixed with blood or pus, nausea, tenesmus, and sometimes fever. Symptoms of the disease resemble Crohn's disease. Patients lose their appetite, lose weight, look weak and exhausted. 17. Whipple's disease. The disease is associated with damage to the intestinal villi and impaired absorption of nutrients. This is a rare disease that manifests itself as weight loss, abdominal pain, diarrhea, steatorrhea, joint pain, fever, swollen lymph nodes, hyperpigmentation and enlarged spleen. In young children, weight loss can be caused by the so-called FTT syndrome (nutritional underdevelopment). Significant weight loss in children may be associated with diabetes. Chronic, progressive weight loss in children is often caused by starvation and poor diet. In older people, slow, gradual weight loss may be associated with aging of the body, a decrease muscle mass. Other possible reasons- difficulty chewing food, loss of teeth, alcoholism and psychiatric disorders. Rapid weight loss for unknown reasons in older adults is statistically associated with a high risk of premature death or disability. Konstantin Mokanov If you are losing weight rapidly and uncontrollably without... visible reasons and effort, it can be extremely dangerous factor, requiring timely diagnosis and comprehensive treatment. Description of fast weight lossRapid weight loss usually means sharp decline body weight and visual emaciation of a person. At the same time external factors There are no conditions that contribute to this symptom: the patient does not engage in active sports, continues to eat well and leads a normal lifestyle. In this case, the patient’s state of health may be normal for some time, but after a certain period of time, he feels weakness, possibly intoxication, a high temperature and other symptoms of a disease appear. ReasonsThe main mechanisms of this process include inadequate poor nutrition or complete starvation, sharply increased needs of the body after exercise and illness, as well as a significant decrease in the absorption of nutrients into the body and hypermetabolism, in which essential vitamins, minerals, fats, proteins, carbohydrates are excreted naturally without their penetration into the body.
Possible diseasesA sharp decrease in body weight, as mentioned above, can be caused by a huge range of diseases and negative conditions. Here are just a few of them:
What to do and how to stop?If the diagnosis does not reveal serious health problems, then it is necessary to apply a number of physiological procedures to normalize metabolism and systematize the diet.
If sudden weight loss is associated with stress or emotional tension, you should:
If your problem is still related to illness, then you should definitely visit a doctor, especially in the case when you have been rapidly losing weight for more than a month, there are other ailments, and your total body weight is 15-20 percent less than average. Are you suddenly losing weight, and at the same time there is a constant urge to vomit, and nausea does not go away even after using medications? There may be several reasons for this, and all of them are related to possible manifestations of disease. The combination of the two above symptoms is characteristic of:
Weight loss and feverRapid and sudden weight loss, as well as the high temperature that accompanies this process, usually indicates the presence in the body of diseases such as ulcerative colitis, gastroenteritis or pulmonary tuberculosis. Quite often, these symptoms indicate extreme exhaustion of the entire body or a chronic lack of fluid that nourishes all body systems. Smooth dynamic weight loss with increasing amplitude, as well as constant low-grade fever, increasing in the evenings, may indicate the development of oncology and cancerous tumors. Weight loss during pregnancy
Weight loss during pregnancy in the first trimester is considered normal if it is accompanied by toxicosis. During this period expectant mother experiences regular vomiting, aversion to certain types of food, and general weakness. Typically, toxicosis goes away by 20-22 weeks and, from a physiological point of view, does not harm the baby or the fair sex. However, if toxicosis significantly drags on or you lose weight without any visible reason for a long period of time, and especially in the second and third trimester, then this is a reason to urgently consult a doctor, who, using a comprehensive diagnostic method, will help determine the real reason weight loss. Weight loss under stressStressful situations, depression, as well as various neurological conditions can provoke both obesity and significant sudden weight loss. In some cases, these conditions provoke the development of anorexia, especially if they are caused deliberately in an attempt to reduce weight by provoking vomiting after meals. The problem can only be eliminated by qualified help from specialists who will prescribe appropriate medication, physiological procedures and recommend psychological help. Carefully and carefully monitor your own health, prevent the development of diseases and always be happy! Useful video
Weight loss- a sharp spontaneous decrease in body mass index over a wide range. Despite the often-used definition of “unreasonable weight loss,” it is never truly unexplained. The factors are either pathological (which happens more often) or physiological. According to medical statistics, approximately 15% of healthy men experience the described problem. Another 15% suffer from endocrine and other pathologies and do not suspect it until certain point. Why does the weight seem healthy man starts to decline? Sudden weight loss is an alarming symptom that requires immediate medical attention. DietThe most obvious answer to the question of why weight drops sharply may be simple: diet. A certain diet is not always a conscious choice of a person: a revision of the diet is possible for objective reasons, a banal lack of time for food, and the like. If a man is obese, but there are no metabolic problems, weight can decrease rapidly. In the first few days, the mass becomes smaller due to the convergence of swelling. You shouldn’t be afraid of such sudden weight loss - it’s completely physiological. However, you should not lose weight too quickly: this can lead to the appearance of stretch marks and skin problems. Aesthetic medicine is not cheap, and it is almost impossible to cope with the problem on your own. The nutritional factor and dietary errors are one of the main reasons. Psycho-emotional stressStress, depression. Prolonged psycho-emotional stress is quite capable of causing unplanned weight loss. In this case, two factors play a role:
Alcoholism and smoking impair metabolism in the body, which leads to weight loss Bad habitsSmoking and alcohol abuse. As a result of smoking and drinking excessive amounts of alcohol, lipid metabolism in the body is disrupted. Nutrients cease to be absorbed normally, and a deficiency of many important compounds occurs. This doesn't happen right away. The factor is encountered by smokers and alcoholics “with experience” when a physiological dependence develops. DiseasesWorm infestation CancerEveryone knows that advanced cancer causes dramatic weight loss. The cancer process is a huge stress for the body. Malignant cellular structures are characterized by great “gluttony”. In later stages, the proliferative activity of pathogenic tissues and cells increases so much that all nutrients are required for their own growth. In addition, the body desperately mobilizes all the body's reserves to restore function and strengthen the immune system. Hence the sharp weight loss and painful thinness of cancer patients. Pathologies of the gastrointestinal tractGastritis, ulcers, hepatitis, cholecystitis in an advanced state lead to the impossibility of normal absorption of nutrients. There is a deficiency of carbohydrates and fats. This condition is fraught with loss normal weight bodies. Diabetes mellitus and other endocrine pathologies- a real disaster for the body. Normal insulin synthesis is disrupted, glucose is constantly elevated, and a total disturbance of lipid metabolism is observed. Often this condition leads to obesity, but in 20% of cases (approximate data) the opposite effect is observed. The cause of weight loss can be and. The thyroid gland acts as a kind of cauldron of the human body. If the “heating boiler” begins to work too intensely, the body produces too much energy and, accordingly, heat. Such rapid energy metabolism requires a lot of resources, which the body draws by destroying fat deposits. A patient with hyperthyroidism experiences a constant feeling of heat, neck relief is measured, exophthalmos (bulging eyes), and body temperature rises. Problems of infectious originInfectious diseases “undermine” the body from the inside. The more serious the disease, the more the body mobilizes all its resources. The most serious disease in this group is tuberculosis. If you experience: cough, hemoptysis, difficulty breathing, you need to think about your own health. Weight loss is also typical for HIV infection in the later stages.
What to do if your weight has dropped suddenly?It is recommended to immediately contact a specialist. First of all, consultation with a therapist is indicated. Then an endocrinologist or gastroenterologist. Problems of endocrinological and gastroenterological profiles are most common. Consultations with an infectious disease specialist or oncologist may be required. Next, you need to undergo a full course of examination. Depending on the type of problem, we can talk about:
It is necessary to promptly identify the factor that caused weight loss. If all tests are negative, the cause should be sought in the nutritional component - poor nutrition. ConclusionsWeight loss – serious sign, often indicating the presence of pathological processes in the body. What kind they are and how serious they are - these questions must be answered by a doctor. It is impossible to figure it out on your own. Losing weight is a dream that both men and women strive for. However, the long-awaited weight loss does not always bring joy. Sometimes the phenomenon occurs suddenly and inexplicably, accompanied by decreased appetite, weakness and other unpleasant symptoms. To exclude serious illnesses, you need to listen carefully to your body and find out the reasons for severe weight loss. Reasons for rapid weight lossA slight fluctuation in weight within 1-2 kilograms indicates a tendency to edema, but in principle is considered normal. It’s wonderful if excess weight goes away when you fall in love or other joyful events, but if there are no such circumstances, and the weight invariably melts away in men and women, it’s worth thinking about why this happens. Sudden unexplained weight loss may indicate various pathological processes in the body. They vary in degree of danger, but under any circumstances require close attention. Among the reasons this phenomenon The following circumstances stand out:
It should be taken into account that often the patient has several prerequisites for sudden weight loss, which are expressed to varying degrees. You can take the first steps towards identifying the cause yourself, but if necessary, it is advisable to consult a doctor. The difficulty is that a person does not always clearly understand which doctor to contact when losing weight. You can start with a therapist who will conduct an initial diagnosis and, if necessary, refer you to a specialist. If a decision needs to be made quickly, the following knowledge about medical specialists will help:
Nowadays, few people like to go to the clinic and undergo many examinations. However, in some cases, it is better to find the time and energy to visit a doctor rather than experience many complications. What to do if you experience sudden weight lossSevere diseases require specific treatment in a hospital setting. If it is possible to independently resolve the issue of sudden weight loss, then a complex of medications is required that normalizes the functioning of all organs and systems of the body. Drug therapy In addition, simple daily procedures will help block weight loss and work up an appetite:
Folk remedies in the fight against weight lossThe following traditional medicine recipes will help you restore weight lost due to loss of appetite:  Prevention of the problemFor many people, losing weight is the leitmotif of their whole life, but there are also those for whom a sharp decrease in body weight for no apparent reason is part of the symptoms of any illness. Constantly taking care of your health will help you avoid this phenomenon. It must be comprehensive to exclude all provoking factors. Preventing the unpleasant consequences of a whole range of pathologies is not as difficult as it might seem. To do this, just stick to simple rules: eat small portions and do not overindulge in junk food, exercise and spend enough time outdoors, and sleep at least 8 hours a day and do not ignore your right to annual leave.
|
| Read: |
|---|
Popular:
Rassolnik with carrots and onions
|
New
- Cottage cheese casserole with apples
- Jellied pork ears recipe Why do you put pig ears in jellied meat?
- Canned saury: the benefits and harms of a famous seafood
- Gemini zodiac sign compatibility with other love signs
- Career Horoscope for April Aquarius
- Why see a snake on the road
- Successful combinations of numbers according to Feng Shui
- Who are godparents?
- Who has an advantage when downsizing?
- Can the full moon drive you crazy?




 The factors that cause uncontrolled weight loss play a very important role, since identifying them will help solve the problem.
The factors that cause uncontrolled weight loss play a very important role, since identifying them will help solve the problem.