Sections of the site
Editor's Choice:
- Spring is the time to bloom quotes
- How to get rid of uterine polyps?
- Riddles, proverbs, sayings, stories and poems about linden Properties of linden tree
- Hour of "massacre" Capture of the Winter Palace
- Ulrich Chairman of the Military Collegium of the Supreme Court of the USSR
- John Cabot - discovery of North America 1497 John Cabot discovery
- Who ruled after the wicket? Ivan I Danilovich Kalita. Biography. Origin and nickname
- Main events of the first Russian revolution
- Abstract to the approximate basic educational program of preschool education “Discovery” Educational program of preschool education discovery
- Cycle of lessons "geography for kids"
Advertising
| How many Russian empires were there? The "longest" states and empires in history |
|
The word "empire" in Lately everyone knows it, it has even become fashionable. It bears a reflection of its former grandeur and luxury. What is an empire? Is this promising?Dictionaries and encyclopedias offer the basic meaning of the word “empire” (from the Latin word “imperium” - power), the meaning of which, without going into boring details and without resorting to dry scientific vocabulary, comes down to the following. Firstly, an empire is a monarchy headed by an emperor or empress (Roman However, for a state to become an empire, it is not enough for its ruler to simply be called an emperor. The existence of an empire presupposes the presence of sufficiently vast controlled territories and peoples, strong centralized power (authoritarian or totalitarian). And if tomorrow Prince Hans-Adam II calls himself emperor, this will not change the essence. government system Liechtenstein (whose population is less than forty thousand people), and it will not be possible to claim that this small principality is an empire (as a form of state). Not less importantSecondly, countries that have impressive colonial possessions are often called empires. In this case, the presence of an emperor is not at all necessary. For example, the English kings were never called emperors, but for almost five centuries they led the British Empire, which included not only Great Britain, but also big number colonies and dominions. The great empires of the world forever etched their names in the tablets of history, but where did they end? Roman Empire (27 BC - 476)Formally, the first emperor in the history of civilization is considered to be Gaius Julius Caesar (100 - 44 BC), who was previously a consul and then declared dictator for life. Realizing the need for serious reforms, Caesar passed laws that changed the political system Ancient Rome. The role of the People's Assembly was lost, the Senate was replenished with Caesar's supporters, which granted Caesar the title of emperor with the right to pass it on to his descendants. Caesar began minting gold coins with his own image. His desire for unlimited power led to a conspiracy of senators (44 BC), organized by Marcus Brutus and Gaius Cassius. In fact, the first emperor was Caesar's nephew, Octavian Augustus (63 BC - 14 AD). The title of emperor in those days denoted the supreme military leader who achieved significant victories. Formally, it still existed, and Augustus himself was called princeps (“first among equals”), but it was under Octavian that the republic acquired the features of a monarchy similar to the eastern despotic states. In 284, Emperor Diocletian (245 - 313) initiated reforms that finally turned the former Roman Republic into an empire. From then on, the emperor began to be called dominus - master. In 395, the state was divided into two parts - Eastern (capital - Constantinople) and Western (capital - Rome) - each of which was headed by its own emperor. Such was the will of Emperor Theodosius, who, on the eve of his death, divided the state between his sons. IN last period During its existence, the Western Empire was subject to constant invasions by barbarians, and in 476 the once powerful state was finally defeated by the barbarian commander Odoacer (about 431 - 496), who would rule only Italy, renouncing both the title of emperor and other possessions of the Roman Empire . After the fall of Rome, great empires would arise one after another.
Byzantine Empire (IV - XV centuries)The Byzantine Empire originated from the Eastern Roman Empire. When Odoacer overthrew the latter, he took away the dignity of power from him and sent them to Constantinople. There is only one Sun on earth, and there should also be one emperor - this is approximately the meaning attached to this act. located at the junction of Europe, Asia and Africa, its borders extended from the Euphrates to the Danube. Christianity played a major role in the strengthening of Byzantium, which in 381 became the state religion of the entire Roman Empire. The Fathers of the Church argued that thanks to faith, not only a person is saved, but also society itself. Consequently, Byzantium is under the protection of the Lord and is obliged to lead other nations to salvation. Secular and spiritual power must be united in the name of a single goal. The Byzantine Empire is a state in which the idea of imperial power took on its most mature form. God is the ruler of the entire Universe, and the emperor presides over the Earthly Kingdom. Therefore, the power of the emperor is protected by God and is sacred. Byzantine Emperor had practically unlimited power, he determined the internal and foreign policy, was the commander-in-chief of the army, the highest judge and at the same time a legislator. The Emperor of Byzantium is not only the head of state, but also the head of the Church, so he had to set an example of exemplary Christian piety. It is curious that the power of the emperor here was not hereditary from a legal point of view. The history of Byzantium knows examples when a person became its emperor not because of a crowned birth, but based on the results of his real merits.
Ottoman (Ottoman) Empire (1299 - 1922)Usually historians count its existence from 1299, when the Ottoman state arose in the north-west of Anatolia, founded by its first Sultan Osman, the founder of the new dynasty. Soon Osman would conquer the entire west of Asia Minor, which would become a powerful platform for the further expansion of the Turkic tribes. It can be said that Ottoman Empire- This is Türkiye during the Sultanate period. But strictly speaking, the empire here emerged only in the 15th - 16th centuries, when Turkish conquests in Europe, Asia and Africa became very significant. Its heyday coincided with the collapse of the Byzantine Empire. This, of course, is not accidental: if it has decreased somewhere, then it will certainly increase elsewhere, as the law of conservation of energy and power on the Eurasian continent says. In the spring of 1453, as a result of a long siege and bloody battles, the troops of the Ottoman Turks under the leadership of Sultan Mehmed II occupied the capital of Byzantium, Constantinople. This victory would ensure that the Turks would secure a dominant position in the eastern Mediterranean for many years to come. The capital of the Ottoman Empire will be Constantinople (Istanbul). Highest point The Ottoman Empire reached its influence and prosperity in the 16th century - during the reign of Suleiman I the Magnificent. By the beginning of the 17th century, the Ottoman state would become one of the most powerful in the world. The Empire controlled almost all of South-Eastern Europe, North Africa and Western Asia, it consisted of 32 provinces and many tributary states. The collapse of the Ottoman Empire will occur as a result of the First World War. Being allies of Germany, the Turks would be defeated, the sultanate would be abolished in 1922, and Turkey would become a republic in 1923.
British Empire (1497 - 1949)The British Empire is the largest colonial state in the entire history of civilization. In the 30s of the twentieth century, the territory of the United Kingdom accounted for almost a quarter of the earth's landmass, and its population was a quarter of those living on the planet (it is no coincidence that English language has become the most authoritative language in the world). England's European conquests began with the invasion of Ireland, and intercontinental conquests with the capture of Newfoundland (1583), which became a springboard for expansion in North America. The success of British colonization was facilitated by the successful imperialist war that England waged with Spain, France, and Holland. In the very early XVII century, Britain's penetration into India will begin, and later England will take on Australia and New Zealand, North, Tropical and South Africa.
Britain and the coloniesAfter World War I, the League of Nations would give the United Kingdom a mandate to govern some of the former Ottoman colonies (including Iran and Palestine). However, the results of World War II significantly shifted the emphasis on the colonial issue. Britain, although it was among the winners, was forced to take out a huge loan from the United States to avoid bankruptcy. The USSR and the USA - the largest players in the political arena - were opponents of colonization. Meanwhile, liberation sentiments intensified in the colonies. In this situation, it was too difficult and expensive to maintain colonial rule. Unlike Portugal and France, England did not do this and transferred power to local governments. At the moment, Great Britain continues to maintain dominance over 14 territories.
Russian Empire (1721 - 1917)After the end of the Northern War, when new lands and access to the Baltic were secured, Tsar Peter I accepted the title of Emperor of All Russia at the request of the Senate, the highest body of state power established ten years earlier. In terms of area, the Russian Empire became the third (after the British and Mongolian empires) of ever existing state entities. Before the appearance of the State Duma in 1905, the power of the Russian emperor was not limited by anything except Orthodox norms. Peter I, who strengthened the country, divided Russia into eight provinces. During the time of Catherine II there were 50 of them, and by 1917, as a result of territorial expansion, their number increased to 78. Russia is an empire that included a number of modern sovereign states (Finland, Belarus, Ukraine, Transcaucasia and Central Asia). As a result February Revolution In 1917, the reign of the dynasty of Russian emperors, the Romanovs, ended, and in September of the same year, Russia was proclaimed a republic.
Centrifugal tendencies are to blameAs we see, all the great empires collapsed. The centripetal forces that create them are sooner or later replaced by centrifugal tendencies, leading these states, if not to complete collapse, then to disintegration. Seizing power must be the dream of at least half of aspiring supervillains. However, some more benevolent (which is doubtful) people try to do this the old-fashioned way: exploration, colonization, conquest, and sometimes (okay - occasionally) even mutually beneficial policies. Although no one had yet been able to openly seize power (shadow communities don't count), the age of empires was certainly not boring, and impressive progress was made as recently as the late 1900s. Let's start all the way from 500 BC and go through it in chronological order until modern times. Here are 25 of the greatest and most powerful empires in the history of mankind! 25. Achaemenid Power - around 500 BC. As the 18th largest empire in history, the Achaemenid Power (also called the first Persian Empire) is already impressive. At the peak of its rise around 550 BC. they occupied an area of 31.6 million km², including the vast majority of the countries of the Middle East and regions of Russia. Even more impressively, under Cyrus II the Great, the empire had a comprehensive social infrastructure, including roads and a postal service, that other empires would later strive to surpass. 24. Macedonian Empire - around 323 BC At its peak, the Macedonian Empire occupied almost 3.5% of the entire world, making it the 21st largest empire in history (and second largest after the Persian conquest). 23. Mauryan Empire - around 250 BC At its height, under a benevolent and diplomatic ruler known as Ashok the Great, the Mauryan Empire covered an area of almost 5 million km², making it the 23rd largest empire in history. 22. Xiongnu Empire - around 209 BC At its height, the Xiongnu Empire occupied more than 6% of the entire world's territory, becoming the 10th largest empire in human history. They were so irresistible that it took years of negotiations, arranged marriages, and concessions by the Han Dynasty to keep them from being conquered. 21. Western Han Dynasty - around 50 BC The Western Han Dynasty included the major diplomatic achievements of Zhang Qian, who established contacts with states as far west as the Roman Empire and established the famous Silk Road trade route. 20. Eastern Han Dynasty - around 100 AD 19. Roman Empire - around 117 AD Indeed, at its peak in 117 AD. it was the most extensive and social structure in Western civilization, but even then the Romans occupied a total of only 5 million km² of land, making them the 24th largest empire in history. In this case, it is not a question of quantity, but of quality, since the influence of the Roman Empire affected almost every aspect of Western civilization. 18. Turkic Khaganate - around 557 AD Like the Xiongnu almost six centuries earlier, they expanded to rule vast areas of Central Asia, including the lucrative trade along the Silk Road. By 557 AD they became the 15th largest empire in history, controlling 4.03% of the entire world's territory (much more than the Roman Empire's 3.36%). 17. Righteous Caliphate - around 655 AD Having subjugated or allied with various Arab tribes, the caliphate embarked on a conquest that led to the dominance of Egypt, Syria, and the entire Persian Empire. At its best period in 655 AD. The Righteous Caliphate was the 14th largest empire, covering 6.4 million km² of territory in the Middle East. 16. Umayyad Caliphate - around 720 AD Having a comprehensive social structure, consisting of 29% of the total world population (62 million people) and 7.45% of the entire world land area, the Umayyad Caliphate became the 8th largest empire in modern history and the largest empire in the world, which only existed until 720 AD. 15. Abbasid Caliphate - around 750 AD They claimed that their lineage was closer to the Prophet Muhammad, so they were his true heirs. After successfully seizing power in 750 AD. they started" golden era", which lasted almost 400 years and included a strong alliance with China. Although their empire was no larger than the Umayyad Caliphate, it lasted for a long period, successfully controlling 11.1 million km², making them the 7th largest empire in human history until its capture by Genghis Khan in 1206. 14. Tibetan Empire - around 800 AD Thanks to diplomacy and impressive military power, the Tibetan Empire lasted for more than 200 years. It is ironic that the growing influence of Buddhist teachings ultimately provoked civil war which split the empire. 13. Tang Dynasty - around 820 AD Less significant than other Chinese dynasties from a historical perspective, the Tang Dynasty lasted for almost three centuries (618 to 907 AD), inhabiting 3.6% of the total world area and ranking as the 20th largest empire in the world. history of mankind. 12. Mongol Empire - around 1270 For comparison, this is more than 4 times the size of the Roman Empire and just under 3 times the size of the modern United States, making the Mongol Empire the 2nd largest empire in human history. 11. Golden Horde - around 1310 Due to the sheer size and power of the original empire, even its individual domains were impressively powerful. In the next generation after the Mongol Empire reached its peak, it became an independent entity. Even on its own, by 1310, it was the 16th largest empire in history and controlled a still impressive 4.03% of the world (about a quarter of the world's land). Mongol Empire). 10. Yuan Dynasty - around 1310 By 1310, it had become the largest fragment of the previous Mongol Empire and the 9th largest empire in human history, with 11 million km² of land in its possession. Unfortunately, uprisings in the mid-14th century led to the final overthrow of the Yuan in 1368, making the dynasty the shortest-lived in Chinese history. 9. Ming Dynasty (Great Ming Empire) - around 1450 It is perhaps best known for building China's first navy, which enabled maritime expeditions and stimulated successful regional maritime trade. 8. Ottoman Empire - circa 1683 Beginning just before 1300, the Ottoman Empire was able to secure its place between the eastern and western worlds for more than six centuries. After defeat in World War I, the empire was destroyed, resulting in the establishment of the Turkish Republic in 1922. 7. Qing Dynasty - circa 1790 Almost three centuries passed before local uprisings forced last emperor abdicate the throne, and the Republic of China was formed in 1912. 6. Spanish Empire - circa 1810 Through numerous maritime conquests, they controlled a huge percentage of territory in both North and South America, as well as virtually all of the Caribbean, parts of Africa, Europe, southern Pacific Ocean and even some cities along the coast of the Middle East. 5. Portuguese Colonial Empire - circa 1820 However, it never achieved the same massive dominance as the Spanish Empire. With 3.69% of the Earth's territory under its control, it is the 19th largest empire in history. However, it is the longest-lived modern European colonial empire, lasting six centuries and just shy of the new millennium (the Portuguese Empire officially ceased to exist on December 20, 1999). 4. Brazilian Empire - circa 1889 After successfully resolving these conflicts, the Brazilian Empire began its "golden age" and quickly became known throughout the world as a progressive and modern nation. By the 1880s, the empire represented most of South America, covering an area of 8.5 million km², making it the 11th largest empire in human history. 3. Russian Empire - circa 1895 At its height in 1895, the population of the Russian Empire grew from 15.5 million to 170 million people living in an area of almost 23.3 million km². With the addition of the Baltic states, Poland, Finland and more significant Asian territories to its territory, the Russian Empire became the 3rd largest in the history of mankind. 2. Second French Colonial Empire - circa 1920 This made the empire at its height the 6th largest in history, as its population accounted for 5% of the entire world population, and it lived on 7.7% of the Earth's territory. 1. British Empire - circa 1920 For more than a century, Britain was the world's premier superpower and controlled 23% of the world's population. As a result of massive expansion around the world, their cultural and linguistic heritage can be found in almost every developed culture on the ground. Most consider the official handover of Hong Kong to China in 1997 to be the official end of the British Empire. Although if you look at the world stage, the UK still controls the largest part of the world... they just do it very smartly and more progressively. Perhaps this is world domination... just done well. The history of mankind is a continuous struggle for territorial dominance. Great empires either appeared on the political map of the world or disappeared from it. Some of them were destined to leave an indelible mark behind them. Persian Empire (Achaemenid Empire, 550 – 330 BC)Cyrus II is considered the founder of the Persian Empire. He began his conquests in 550 BC. e. with the subjugation of Media, after which Armenia, Parthia, Cappadocia and the Lydian kingdom were conquered. Did not become an obstacle to the expansion of the empire of Cyrus and Babylon, whose powerful walls fell in 539 BC. e. While conquering neighboring territories, the Persians tried not to destroy the conquered cities, but, if possible, to preserve them. Cyrus restored captured Jerusalem, like many Phoenician cities, facilitating the return of Jews from Babylonian captivity. The Persian Empire under Cyrus extended its possessions from Central Asia to the Aegean Sea. Only Egypt remained unconquered. The country of the pharaohs submitted to the heir of Cyrus, Cambyses II. However, the empire reached its peak under Darius I, who switched from conquests to domestic policy. In particular, the king divided the empire into 20 satrapies, which completely coincided with the territories of the captured states. Roman Empire (27 BC – 476)
Ancient Rome was the first state in which the ruler received the title of emperor. Beginning with Octavian Augustus, the 500-year history of the Roman Empire had a direct impact on European civilization and also left a cultural mark on the countries of North Africa and the Middle East. At the height of the Roman Empire, its territories extended from the British Isles to the Persian Gulf. According to historians, by 117 the population of the empire reached 88 million people, which was approximately 25% of the total number of inhabitants of the planet. Architecture, construction, art, law, economics, military affairs, the principles of government of Ancient Rome - this is what the foundation of the entire European civilization. It was in imperial Rome that Christianity acquired the status state religion and began to spread throughout the world. Byzantine Empire (395 – 1453)
The Byzantine Empire has no equal in the length of its history. Originating at the end of antiquity, it existed until the end of the European Middle Ages. For more than a thousand years, Byzantium was a kind of connecting link between the civilizations of the East and West, influencing both the states of Europe and Asia Minor. But if Western European and Middle Eastern countries inherited the richest material culture Byzantium, the Old Russian state turned out to be the successor of its spirituality. Constantinople fell, but Orthodox world found its new capital in Moscow. Located at the crossroads of trade routes, rich Byzantium was a coveted land for neighboring states. Having reached its maximum borders in the first centuries after the collapse of the Roman Empire, then it was forced to defend its possessions. In 1453, Byzantium could not resist a more powerful enemy - the Ottoman Empire. With the capture of Constantinople, the road to Europe was opened for the Turks. Arab Caliphate (632-1258)
As a result of Muslim conquests in the 7th–9th centuries, the theocratic Islamic state of the Arab Caliphate arose in the entire Middle Eastern region, as well as in certain regions of Transcaucasia, Central Asia, North Africa and Spain. The period of the Caliphate went down in history as the “Golden Age of Islam”, as the time of the highest flowering of Islamic science and culture. In 1036, the invasion of the Seljuk Turks was disastrous for the Caliphate, but the defeat of the Islamic state was completed by the Mongols. Caliph An-Nasir, wanting to expand his possessions, turned to Genghis Khan for help, and unknowingly opened the way for the destruction of the Muslim East by a Mongol horde of thousands. Mongol Empire (1206–1368)
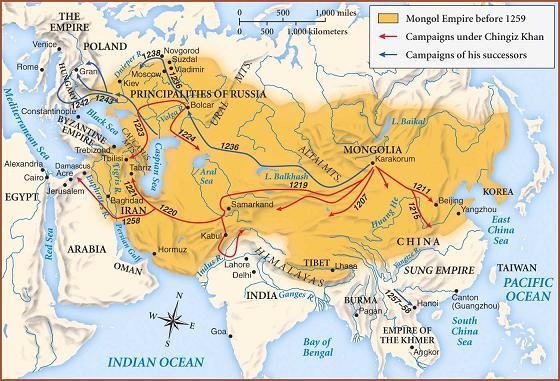
The Mongol Empire is the largest in terms of territory public education in history. During the period of its power - by the end of the 13th century, the empire extended from Sea of Japan to the banks of the Danube. The total area of the Mongols' possessions reached 38 million square meters. km. Given the enormous size of the empire, managing it from the capital, Karakorum, was almost impossible. It is no coincidence that after the death of Genghis Khan in 1227, the process of gradual division of the conquered territories into separate uluses began, the most significant of which became the Golden Horde. The economic policy of the Mongols in the occupied lands was primitive: its essence boiled down to the imposition of tribute on the conquered peoples. Everything collected went to support the needs of a huge army, according to some sources, reaching half a million people. The Mongol cavalry was the most deadly weapon of the Genghisids, which not many armies could resist. Holy Roman Empire (962-1806)
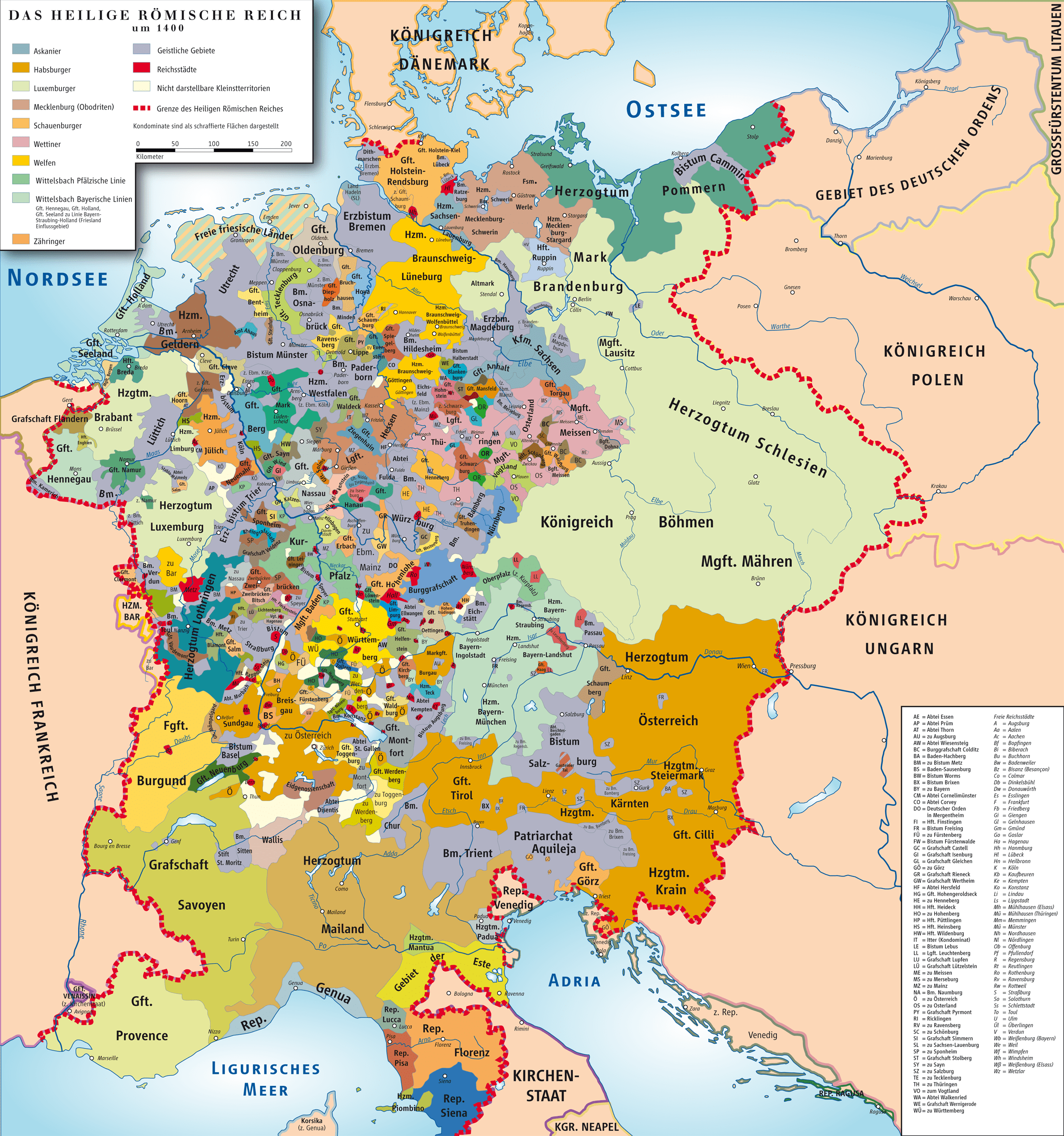
The Holy Roman Empire is an interstate entity that existed in Europe from 962 to 1806. The core of the empire was Germany, which was joined by the Czech Republic, Italy, the Netherlands, as well as some regions of France during the period of the highest prosperity of the state. Ottoman Empire (1299–1922)
In 1299, Osman I created a Turkic state in the Middle East, which was destined to exist for more than 600 years and radically influence the fate of the countries of the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions. The fall of Constantinople in 1453 marked the date when the Ottoman Empire finally gained a foothold in Europe. The period of the greatest power of the Ottoman Empire occurred in the 16th-17th centuries, but the state achieved its greatest conquests under Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent. The borders of the empire of Suleiman I extended from Eritrea in the south to the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth in the north, from Algeria in the west to the Caspian Sea in the east. The period from the end of the 16th century to the beginning of the 20th century was marked by bloody military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and Russia. Territorial disputes between the two states mainly revolved around Crimea and Transcaucasia. The First put an end to them World War, as a result of which the Ottoman Empire, divided between the Entente countries, ceased to exist. British Empire (1497¬–1949)
The British Empire is the largest colonial power both in terms of territory and population. The empire reached its greatest scale by the 30s of the 20th century: the land area of the United Kingdom, including its colonies, totaled 34 million 650 thousand square meters. km., which accounted for approximately 22% of the earth's land. Total number The population of the empire reached 480 million people - every fourth inhabitant of the Earth was a subject of the British Crown. The success of British colonial policy was facilitated by many factors: a strong army and navy, developed industry, and the art of diplomacy. The expansion of the empire significantly influenced global geopolitics. First of all, this is the spread of British technology, trade, language, and forms of government throughout the world. Russian Empire (1721–1917)
The history of the Russian Empire dates back to October 22, 1721, after Peter I accepted the title of All-Russian Emperor. From that time until 1905, the monarch who became the head of the state was endowed with absolute power. In terms of area, the Russian Empire was second only to the Mongol and British empires - 21,799,825 square meters. km, and was the second (after British) in terms of population - about 178 million people. Constant expansion of territory – characteristic feature Russian Empire. But if the advance to the east was mostly peaceful, then in the west and south they had their own territorial claims Russia had to prove itself through numerous wars - with Sweden, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Ottoman Empire, Persia, and the British Empire. The growth of the Russian Empire has always been viewed with particular caution by the West. The negative perception of Russia was facilitated by the appearance of the so-called “Testament of Peter the Great,” a document fabricated in 1812 by French political circles. “The Russian state must establish power over all of Europe” is one of the key phrases of the Testament, which will haunt the minds of Europeans for a long time. 03.05.2013 A hundred years ago, countries strived to become the most powerful and developed powers in the world, capturing more and more territories and spreading their influence. This is the top 10 most great empires world in history. They are considered the most important and longest lasting, they were powerful and played an important role in history. The Russian Empire and even the great Macedonian Empire created by Alexander the Great did not make it into the top 10, but it was the first European empire that advanced into Asia and defeated the Persian Empire, and perhaps one of the most powerful in ancient world. But it is believed that these 10 great empires were more important in history, made a greater contribution. Mayan Empire (c.2000 BC-1540 AD)This empire is distinguished by its longevity, its cycle lasted almost 3500 years! This is twice the life of the Roman Empire. So far, scientists know very little about the first 3,000 years, as well as about the mysterious pyramid-like structures scattered throughout the Yucatan Peninsula. Well, is it worth mentioning the famous doomsday calendar? French Empire (1534-1962)
Spanish Empire (1492-1976)
Qing Dynasty (1644-1912)
Umayyad Caliphate (661-750)
Achaemenid Empire (c. 550-330 BC)
Great Ottoman Empire (1299-1922)
Mongol Empire (1206-1368)
British Empire (1603 to 1997)
Greater Roman Empire (27 BC to 1453)
|
Popular:
New
- How to get rid of uterine polyps?
- Riddles, proverbs, sayings, stories and poems about linden Properties of linden tree
- Hour of "massacre" Capture of the Winter Palace
- Ulrich Chairman of the Military Collegium of the Supreme Court of the USSR
- John Cabot - discovery of North America 1497 John Cabot discovery
- Who ruled after the wicket? Ivan I Danilovich Kalita. Biography. Origin and nickname
- Main events of the first Russian revolution
- Abstract to the approximate basic educational program of preschool education “Discovery” Educational program of preschool education discovery
- Cycle of lessons "geography for kids"
- An interactive poster for lessons on the surrounding world was prepared by Svetlana Anatolyevna Grevtsova, a primary school teacher at MBOU SOS.





































 Second largest in history great empire- French colonial empire, occupied 4.9 million square miles and covered almost 1/10 of the total area of the Earth. Her influence made
Second largest in history great empire- French colonial empire, occupied 4.9 million square miles and covered almost 1/10 of the total area of the Earth. Her influence made  One of the first large empires that seized territories in Europe, America, Africa, Asia and Oceania, creating colonies. For hundreds of years it remained one of the most important political and economic forces in the world. The main contribution to history is undoubtedly the discovery of the New World in 1492 and the spread of Christianity in the Western world.
One of the first large empires that seized territories in Europe, America, Africa, Asia and Oceania, creating colonies. For hundreds of years it remained one of the most important political and economic forces in the world. The main contribution to history is undoubtedly the discovery of the New World in 1492 and the spread of Christianity in the Western world. The last ruling dynasty of China in its imperial past. It was founded by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in the territory of modern Manchuria in 1644, quickly grew and developed and eventually, by the 18th century, covered all the territories of modern China, Mongolia and even parts of Siberia. The empire covered an area of more than 5,700,000 square miles. The dynasty was overthrown during the Xinhai Revolution.
The last ruling dynasty of China in its imperial past. It was founded by the Manchu clan Aisin Gioro in the territory of modern Manchuria in 1644, quickly grew and developed and eventually, by the 18th century, covered all the territories of modern China, Mongolia and even parts of Siberia. The empire covered an area of more than 5,700,000 square miles. The dynasty was overthrown during the Xinhai Revolution. One of the fastest growing great empires in history, whose life, however, was just as short. It was founded by one of the four caliphates - the Umayyad Caliphate, after the death of the Prophet Muhammad and served to spread Islam throughout the Middle East and North Africa. Sweeping away everything in its path, Islam seized power in the region and retains it to this day.
One of the fastest growing great empires in history, whose life, however, was just as short. It was founded by one of the four caliphates - the Umayyad Caliphate, after the death of the Prophet Muhammad and served to spread Islam throughout the Middle East and North Africa. Sweeping away everything in its path, Islam seized power in the region and retains it to this day. Most often it is called the Medo-Persian Empire. Stretching from the Indus Valley of modern Pakistan to Libya and the Balkans, this empire is the largest Asian empire in
Most often it is called the Medo-Persian Empire. Stretching from the Indus Valley of modern Pakistan to Libya and the Balkans, this empire is the largest Asian empire in  Became one of the largest and longest-lived great empires of the world in history. At its height (under the rule of Suleiman the Magnificent) in the 16th century, it stretched from the southern borders of the Holy Roman Empire to the Persian Gulf, and from the Caspian Sea to Algeria, effectively holding control over much of southeastern Europe, western Asia and northern Africa. . At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire included no fewer than 32 provinces, along with numerous vassal states. Unfortunately, ethnic and religious tensions and competition from other powers led to a gradual disintegration in the 19th century.
Became one of the largest and longest-lived great empires of the world in history. At its height (under the rule of Suleiman the Magnificent) in the 16th century, it stretched from the southern borders of the Holy Roman Empire to the Persian Gulf, and from the Caspian Sea to Algeria, effectively holding control over much of southeastern Europe, western Asia and northern Africa. . At the beginning of the 17th century, the empire included no fewer than 32 provinces, along with numerous vassal states. Unfortunately, ethnic and religious tensions and competition from other powers led to a gradual disintegration in the 19th century. Despite the fact that the empire lasted only 162 years, the pace at which it grew is frightening. Under the leadership of Genghis Khan (1163-1227), the entire territory from
Despite the fact that the empire lasted only 162 years, the pace at which it grew is frightening. Under the leadership of Genghis Khan (1163-1227), the entire territory from  Despite its short life span of only 400 years, the British Empire (essentially several British Isles) managed to become the largest in history. At its peak in 1922, the empire dominated almost 500 million people (1/5 of the world's population at that time) and covered more than 13 million square meters. miles (1/4 of the Earth's area)! That empire had colonies on all continents of the world. Alas, everything must come to an end. After two world wars, Britain was financially devastated and, after the loss of India in 1947, gradually began to lose influence and colonies.
Despite its short life span of only 400 years, the British Empire (essentially several British Isles) managed to become the largest in history. At its peak in 1922, the empire dominated almost 500 million people (1/5 of the world's population at that time) and covered more than 13 million square meters. miles (1/4 of the Earth's area)! That empire had colonies on all continents of the world. Alas, everything must come to an end. After two world wars, Britain was financially devastated and, after the loss of India in 1947, gradually began to lose influence and colonies. Founded in 27 BC. Octavian Augustus it existed for 1500 years! And it was eventually overthrown by the Turks under the leadership of Mehmed II, who destroyed Constantinople in 1453. For 117 AD heyday came great empire. At this time she was the most powerful on earth, although not the largest in history. The population was 56.8 million people, the territory under its rule was 2,750,000 km². Influence on modern
Founded in 27 BC. Octavian Augustus it existed for 1500 years! And it was eventually overthrown by the Turks under the leadership of Mehmed II, who destroyed Constantinople in 1453. For 117 AD heyday came great empire. At this time she was the most powerful on earth, although not the largest in history. The population was 56.8 million people, the territory under its rule was 2,750,000 km². Influence on modern 




